What is prostate cancer?
What is prostate cancer?
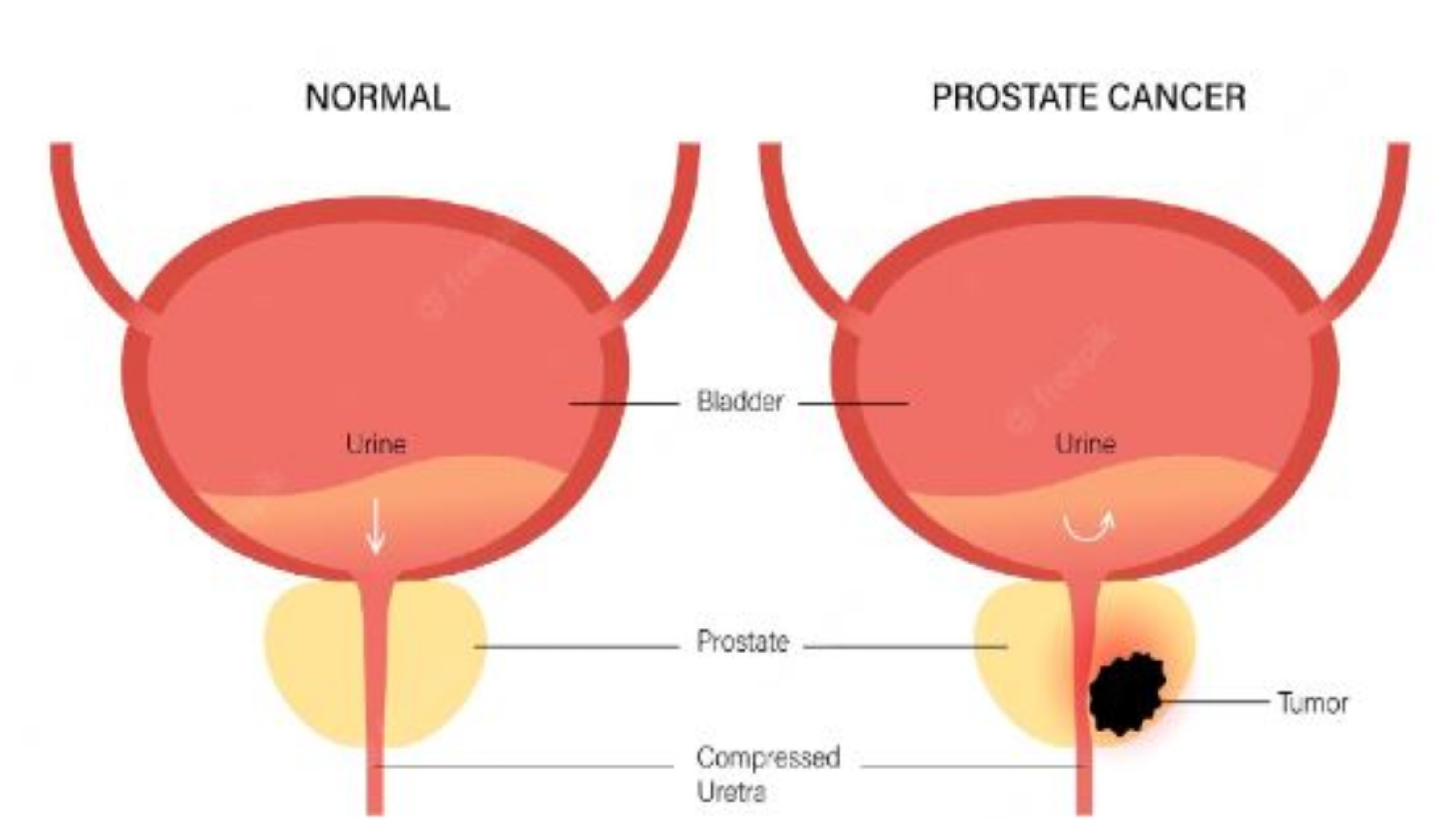
Prostate is gland which is walnut shaped and creates seminal fluid which nutrifies and transports sperms, it is common type and grows slowly within the prostate. Some Prostate Cancers Grow Slowly and need least or no treatment while others grow faster and need better treatment. Alike all types of cancer if Prostate Cancer is detected early when its confined to prostate gland has more possiblities of successful treatment.
In early stages prostate cancer do not show any signs or symptoms but in the further stages it shows following symptoms.
-Trouble urinating
-Decreased force in the stream of urine
-Blood in the urine
-Blood in the semen
-Bone pain
-Losing weight without trying
-Erectile dysfunction
causes of prostate cancer?
The cause of cancer including prostate cancer is not well understood. There are several risk factors for cancer and old age is the most important risk factor for prostate cancer. It was observed that 80% of men above the age of 80 have prostate cancer. There are several hypothesizes regarding cancer. Doctors thought that cancer was a growth disease caused by a random error in cell division and mutations. But everybody did not agree to this concept. Scientists thought that cancer was a virus disease. Another group of scientists thought that cancer was a genetic disease. Some other group of scientists thought that cancer was a metabolic disease. Prof Lloyd J Old described cancer a “somatic cell pregnancy”. I consider cancer a genetically unstable growth evolved while attempting asexual reproduction by mutations, promoted by the gametogenic genes and is seen often when sexual reproduction is stopped as in old age. It was observed that incidence of prostate cancer is less in men when there is frequent ejaculation. Most of the risk factors for prostate cancer ( old age,obesity,use of tobacco and alcohol) are also risk factors for infertility.
What is the diagnosis of prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer diagnosis typically involves a combination of PSA tests, digital rectal exams (DRE), imaging tests (MRI, CT scans), and prostate biopsies. These diagnostic procedures help determine the presence, stage, and aggressiveness of prostate cancer, guiding treatment decisions accordingly.
prostate cancer symptoms:-
There are a number of symptoms that may indicate prostate cancer. Some of the more common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak urine stream or inability to urinate
- Painful urination and ejaculation
- Blood in urine or semen
- Nagging pain in the lower back, hips or pelvis
- Painful ejaculation
Other potential symptoms include:
- Frequent pain or stiffness in lower back, hips, pelvis or thighs
- Dull ache or pain in the groin or legs
- Persistent bone pain or tenderness
- Unintended weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Erectile dysfunction
- Swelling of the legs or feet
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue
- Changes in bowel habits
Preventing prostate cancer may not be entirely possible, but the following lifestyle measures can help reduce your risk:
1. Maintain a healthy weight
2. Exercise regularly
3. Follow a nutritious diet, high in veggies and low in processed meats
4. Avoid smoking and excess alcohol
5. Limit calcium supplements
6. Drink green tea
7. Eat cooked tomatoes and tomato sauce
8. Use healthy fats like olive oil
9. Reduce dairy food intake
10. Limit red meat consumption
11. Eat more fish rich in omega-3 fats
12. Increase soy intake
13. Eat more fruits and veggies high in antioxidants
14. Stay socially active
15. Check medications with doctor that may increase risk
16. Treat prostatitis if present
17. Practice safe sex
18. Get regular screenings for prostate cancer
19. Avoid exposure to certain chemicals
20. Decrease stress
21. Get enough vitamin D
22. Take supplements like selenium
23. Manage other health conditions
24. Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke
25. Limit alcohol intake
26. Drink enough water
27. Protect skin from sun exposure
28. Maintain proper oral health
29. Avoid high-fat diet
30. Reduce sitting time
31. Get 7-8 hours of sleep per night
32. Manage high blood pressure
33. Treat high cholesterol
34. Increase fiber intake
35. Stay mentally stimulated
36. Avoid BPA products
37. Limit grilled meats
38. Reduce refined carbohydrates
39. Drink green tea
40. Exercise pelvic floor muscles
41. Limit sugars and sweeteners
42. Eat cruciferous vegetables
43. Take lycopene supplements
44. Decrease inflammation
45. Balance estrogen levels
46. Try stress management techniques
47. Boost immune system
48. Consume probiotics
49. Follow an anti-cancer diet
50. Listen to your body
Conclusion:-
While prostate cancer cannot always be prevented, understanding its numerous potential symptoms and incorporating lifestyle measures to reduce risk is key for all men. Paying attention to your body, getting regular screenings, and discussing any concerns with your doctor can also aid early detection and treatment. Awareness and proactive healthy living are your best defenses against prostate cancer.
Treatment for Prostate Cancer:-
Different Treatment is practiced at the different stages of prostate cancer
Stage I : At early stage the cancer grows slowly and shows less or no symptoms in this case active surveillance or watchful waiting may be recommended.
Stage II : After the Surveillance if the Gleason score is high, the cancer may be faster growing, so radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy are often recommended or surgery may also be suggested, as well as treatment in clinical trials.
Stage III : Stage III prostate cancer may be treated with external-beam radiation therapy and concurrent hormonal therapy or with surgery, doctors consider hormonal therapy to stop testosterone production.
Stage IV : High-risk or locally advanced prostate cancers have a higher chance of becoming metastatic cancer. There is no cure for metastatic prostate cancer, but it is often treatable for quite some time by experienced doctors. Patient and his family are encouraged to talk about how you feel with doctors, nurses, social workers, or other members of the health care team. It may also be helpful to talk with other patients, such as through a support group or other peer support program.










Post a Comment